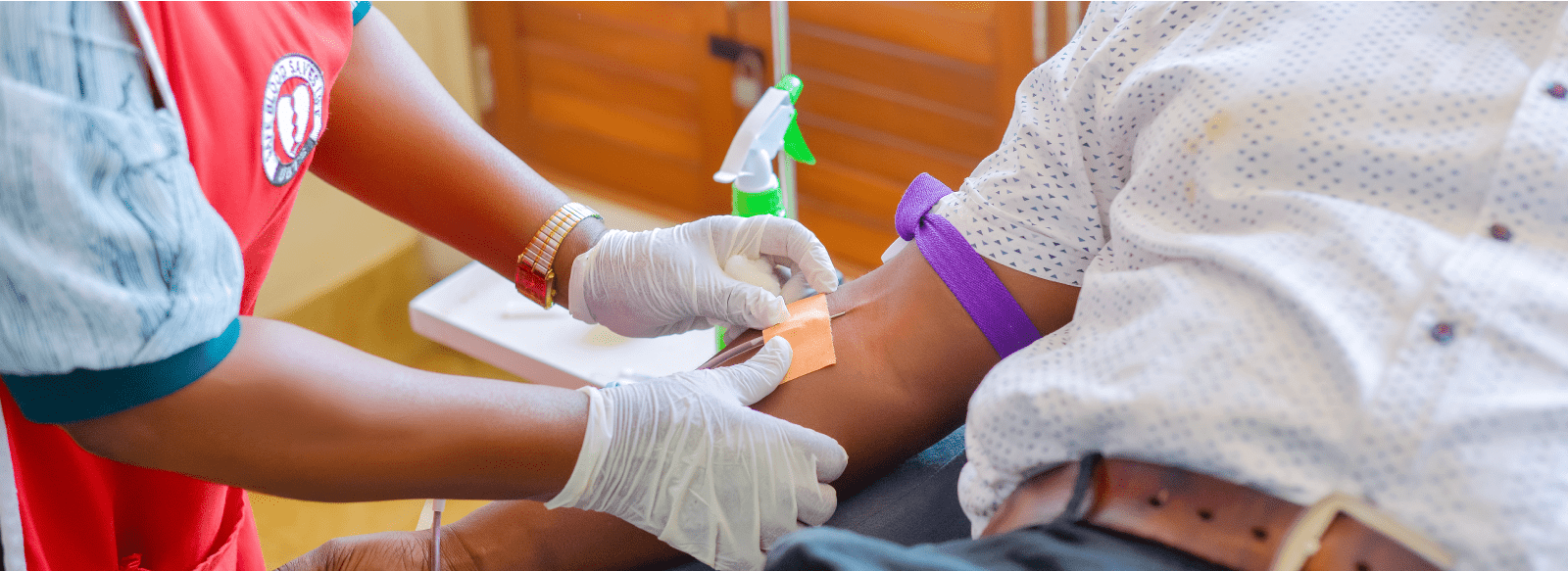
Blood is essential to life. Blood circulates through our body and delivers essential substances like oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells. It also transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. There is no substitute for blood. It cannot be made or manufactured. Generous blood donors are the only source of blood for patients in need of a blood transfusion.
Although all blood is made of the same basic elements, not all blood is alike. In fact, there are eight different common blood types, which are determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens - substances that can trigger an immune response if they are foreign to the body. Since some antigens can trigger a patient's immune system to attack the transfused blood, safe blood transfusions depend on careful blood typing and cross-matching.
There are four major blood groups determined by the presence or absence of two antigens – A and B – on the surface of red blood cells:
Group A,Group B, Group AB,Group O
There are very specific ways in which blood types must be matched for a safe transfusion. See the chart below:
In addition to the A and B antigens, there is a third antigen called the Rh factor, which can be either present (+) or absent ( – ). In general, Rh negative blood is given to Rh-negative patients, and Rh positive blood or Rh negative blood may be given to Rh positive patients.
The universal red cell donor has Type O negative blood type.
The universal plasma donor has Type AB blood type.
It’s inherited. Like eye color, blood type is passed genetically from your parents. Whether your blood group is type A, B, AB or O is based on the blood types of your mother and father.
This chart shows the potential blood types you may inherit.